Allergy symptoms
Symptoms will vary depending on the allergen, but can affect the nose, eyes, throat and skin, as well as worsening asthma or eczema symptoms.
The allergic response can be separated into early and late phases.
- After exposure to the allergen, immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies bind to mast cells in the nasal mucosa7
- This triggers the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators from mast cells7,8
- This inflammatory cascade results in the symptoms of allergic rhinitis within minutes of exposure to the allergen
- Characterised by sneezing, itching, congestion and nasal discharge
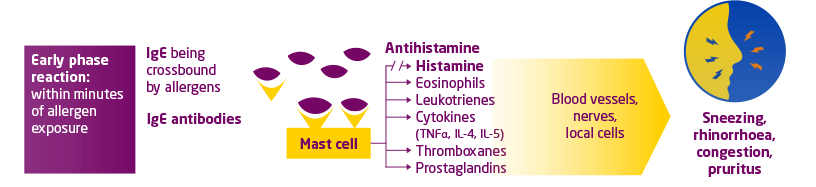
- Occurs within hours of allergen exposure
- Initiated due to inflammatory cascade of the early phase driving adhesion and infiltration of the mucosa by certain cell types
- This 'cellular-driven' inflammatory reaction occurs due to activation of eosinophils, neutrophils, basophils, T lymphocytes and macrophages, which cause a second release of inflammatory mediators
- Symptoms are similar to those of the early phase, but congestion may predominate
- Also reactivates the early-phase mechanisms and symptoms

Most allergic reactions are mild; however, occasionally a severe reaction, or anaphylaxis, can occur. This is a medical emergency and requires urgent medical treatment.
